Whether you’re embarking on your first home building project, purchasing property, or planning renovations, understanding what a site plan is becomes fundamental to your success. A site plan serves as the blueprint that bridges your vision with reality, transforming abstract ideas into tangible construction guidance.
At its core, a site plan is a detailed architectural drawing that provides a bird’s-eye view of your entire property. This comprehensive document illustrates existing conditions, proposed developments, and the relationship between your future home and the surrounding environment. For Australian homeowners and home builders, site plans are not merely helpful documents—they’re legal requirements that ensure compliance with local council regulations and building codes.
What Is a Site Plan? The Foundation of Your Building Project
A site plan, also known as a plot plan or site layout, is a technical document that serves as a communication tool between architects, builders, council authorities, and homeowners. This ensures everyone shares the same vision for your project.
A site plan serves multiple critical functions beyond simple illustration. These drawings demonstrate compliance with zoning requirements, assist in obtaining building permits, guide construction teams during the building process, and provide legal documentation of your property’s development. Essentially, a site plan functions as both a practical tool and a legal document.
Modern site plans incorporate sophisticated surveying techniques and computer-aided design software, resulting in precise measurements and accurate representations. This technological advancement ensures your site plan reflects actual ground conditions and provides reliable information for construction planning.
Essential Components Every Site Plan Must Include
Don't Settle for Less—Build Excellence with Dhursan
Property Boundaries and Legal Descriptions
Every site plan begins with clearly defined property boundaries, marked with precise measurements and bearing information. These boundary lines establish the legal limits of your property and determine where construction can occur. Australian site plans must reference the Certificate of Title and include survey marks, ensuring absolute accuracy in property definition.
Setback requirements form another crucial boundary consideration. Front, side, and rear setbacks dictate the minimum distances between your proposed structures and property lines. These measurements ensure compliance with council requirements and maintain neighbourhood character consistency.
Existing Site Features and Conditions
Comprehensive site analysis requires documenting all existing features on your property. This includes mature trees, existing structures, natural features like rock formations or water bodies, and topographical variations. Understanding what is a site plan means appreciating how these existing elements influence your home design and construction approach.
Utility locations represent critical existing conditions that directly impact construction planning. Your site plan must accurately show the position of electricity meters, gas connections, water mains, sewer lines, and telecommunications infrastructure. This information prevents costly mistakes during excavation and ensures efficient connection of new services.
Proposed Development Elements
The heart of any site plan lies in its proposed development elements. Your future home’s footprint, including all structural components, appears as a scaled representation showing exact positioning relative to boundaries and existing features. This includes the main dwelling, garages, outdoor entertainment areas, and any secondary structures like sheds or studios.
Landscaping elements form an integral part of modern site plans, reflecting the growing emphasis on outdoor living and environmental considerations. Proposed gardens, pathways, retaining walls, pools, and outdoor entertainment areas all require careful planning and accurate representation on your site plan.
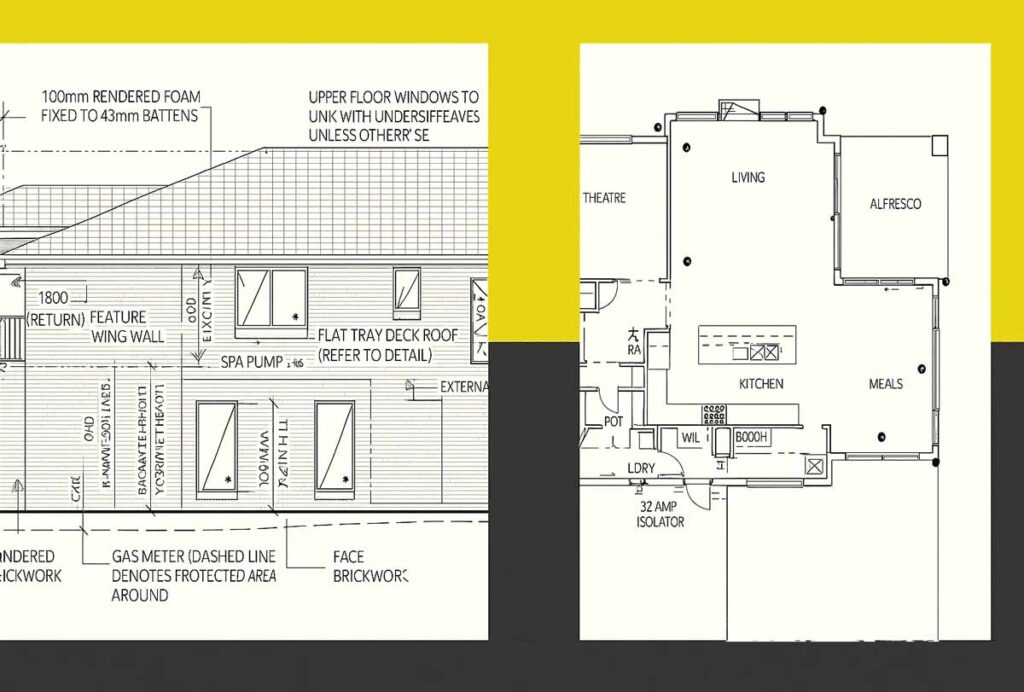
Reading and Interpreting Site Plan Symbols
Understanding Scale and Measurements
Site plans typically use metric scales, commonly 1:100 or 1:200 for residential properties. This means that one millimetre on the drawing represents 100 or 200 millimetres in real life. Understanding scale allows you to visualise actual distances and proportions, making it easier to assess whether your proposed development suits your needs and expectations.
Dimension lines and measurement annotations provide specific distances between key elements. These measurements form the basis for construction layout and must be accurate to ensure proper building positioning and compliance with setback requirements.
Decoding Standard Site Plan Symbols
Site plan symbols follow Australian Standards conventions, ensuring consistency across different professionals and projects. Building outlines typically appear as bold, solid lines, while proposed structures may be shown with different line weights or patterns to distinguish them from existing elements.
Landscaping symbols represent different vegetation types and outdoor features. Trees appear as circles with species notation, while gardens and lawn areas use specific hatching patterns. Understanding these symbols helps you visualise the completed project and assess the balance between built and natural elements.
Site Analysis and Soil Considerations
Conducting Proper Site Analysis
Professional site analysis forms the foundation of successful site planning. This process involves detailed surveys that measure existing levels, identify soil conditions, assess drainage patterns, and evaluate access requirements. Understanding what is a site plan means recognising that accurate site analysis directly influences design decisions and construction costs.
Topographical surveys create contour maps showing natural ground levels across your property. These measurements determine cut and fill requirements, drainage design, and foundation specifications. Steep slopes may require retaining walls or specialised foundation systems, while flat sites might present drainage challenges that need addressing.
Soil Testing and Geotechnical Considerations
Australian building standards require geotechnical assessment for most residential construction projects. Soil tests determine bearing capacity, reactivity levels, and drainage characteristics that influence foundation design and construction methodology. This information appears on your site plan as soil classification symbols and foundation recommendations.
Reactive clay soils, common in many Australian regions, require special attention in site planning. These soils expand and contract with moisture changes, potentially causing structural movement. Your site plan must accommodate these conditions through appropriate foundation design and drainage planning.
Drainage and Stormwater Management
Planning Effective Drainage Systems
Stormwater management represents one of the most critical aspects of site planning, particularly given Australia’s variable rainfall patterns and increasing focus on environmental sustainability. Your site plan must demonstrate how rainwater will be collected, managed, and discharged in compliance with council requirements and environmental best practices.
Downpipe locations, shown as small circles or squares on site plans, indicate where roof water is collected and directed to disposal systems. The positioning of downpipes influences both architectural design and landscape planning, requiring coordination between multiple design disciplines.
Council Requirements and Compliance
Local councils impose specific requirements for stormwater management, often mandating retention systems or water quality treatment before discharge. Your site plan must demonstrate compliance with these requirements, showing detention tanks, infiltration systems, or other approved disposal methods.
On-site detention (OSD) systems have become increasingly common, particularly in urban areas where traditional drainage infrastructure faces capacity constraints. These systems temporarily store stormwater during peak rainfall events, gradually releasing water to prevent downstream flooding.
RELATED: WHAT IS A CERTIFICATE OF BUILDING COMPLIANCE?
Building Setbacks and Compliance Requirements
Understanding Setback Regulations
Building setbacks form the cornerstone of Australian residential planning controls, ensuring adequate separation between structures and maintaining neighbourhood character. Understanding what is a site plan includes comprehending how setback requirements influence your building design and positioning options.
Front setbacks typically range from 6 to 10 metres in established residential areas, though heritage overlays or specific zone requirements may impose different standards. Side and rear setbacks vary according to building height, ensuring adequate light access and privacy for neighbouring properties.
Easements and Restrictions
Utility easements may traverse your property, creating areas where building is restricted or prohibited. These easements ensure access for maintenance of essential services and must be clearly shown on your site plan. Understanding easement implications helps you optimise your building design within available space.
Building envelopes define the three-dimensional space within which construction can occur. These envelopes consider setbacks, height limits, and other planning controls to create a “box” that contains your permitted development. Your site plan must demonstrate that your proposed building fits entirely within this envelope.
RELATED: 10 DIFFERENT TYPES OF BUILDING CONTRACTS
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Incorporating Sustainable Design Principles
Modern site planning increasingly emphasises environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. Solar access considerations influence building orientation and window placement, while prevailing wind patterns affect natural ventilation and outdoor comfort. Your site plan should demonstrate how these environmental factors have been considered in your design approach.
Native vegetation retention and integration of sustainable landscaping practices reflect growing environmental awareness in residential development. Site plans may indicate existing trees to be retained, new native plantings, and water-sensitive urban design elements that reduce environmental impact.
Council Environmental Requirements
Many Australian councils now require consideration of environmental factors in site planning, including tree preservation, biodiversity enhancement, and stormwater quality improvement. Your site plan must demonstrate compliance with these requirements while achieving your development objectives.
Energy efficiency requirements may influence site planning decisions, particularly regarding solar panel placement, building orientation, and natural lighting optimisation. These considerations affect both initial design and long-term operational costs of your home.
Transform Your Vision into Reality with Dhursan Construction
Professional Review and Approval Processes
Working with Design Professionals
Creating an effective site plan requires collaboration between various professionals, including surveyors, architects, engineers, and landscape designers. Each professional contributes specialist knowledge that ensures your site plan addresses all relevant technical and regulatory requirements.
Council approval processes vary across different jurisdictions, but generally require comprehensive documentation demonstrating compliance with planning schemes and building regulations. Understanding what is a site plan means recognising its role in this approval process and ensuring all required information is included.
Common Review Considerations
Planning departments assess site plans against numerous criteria, including compliance with setback requirements, compliance with height limits, adequate car parking provision, appropriate stormwater management, and neighbourhood character compatibility. Addressing these considerations during the design phase prevents delays and revision requirements.
Building surveyors review site plans for compliance with building codes and structural requirements. This review ensures that your proposed development meets safety standards and construction requirements, providing confidence in your building project’s viability.
Your site plan serves as more than a technical document—it represents the foundation of your building dreams transformed into achievable reality. By understanding what is a site plan and mastering its interpretation, you gain the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions throughout your building journey. Whether you’re planning a modest renovation or an ambitious new home, comprehensive site planning ensures your project proceeds smoothly from concept to completion.
Working with experienced professionals and taking time to thoroughly understand your site plan investment pays dividends through reduced construction delays, cost certainty, and confidence that your finished project will meet both your expectations and regulatory requirements. Embrace the site planning process as an opportunity to optimise your development and create the home you’ve always envisioned.